To watch this Pt. 2 as a 6-minute video
To hear this Pt. 2 as a 6-minute podcast
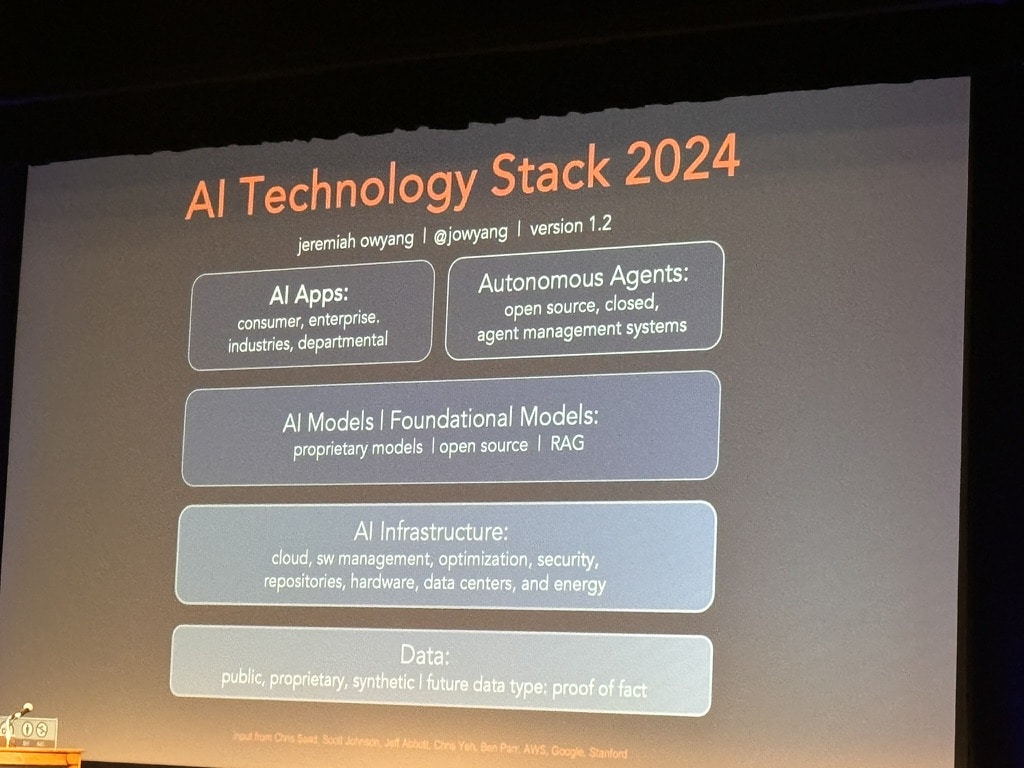
“Co-pilot”: Needs to be prompted by humans, it is asynchronous.
“Agent”: Does not need to be prompted by humans, autonomously synchronous. It loops many models such as RPA, SaaS into one, not just LLM or specific applications.

Jobs that will be replaced by AI (and humans will just do the checking), according to Dr. Muddu Sudhakar, Co-Founder & CEO, Aisera:
A boy who got accepted by UCLA as a freshman asked, from the audience: “I was planning to study computer science, now if software developers are going to be obsolete, what should I study?” The entire audience of about three hundred people all burst out laughing. Dr. Muddu Sudhakar replied: “Pursue what you are passionate about. Go to UCLA.”
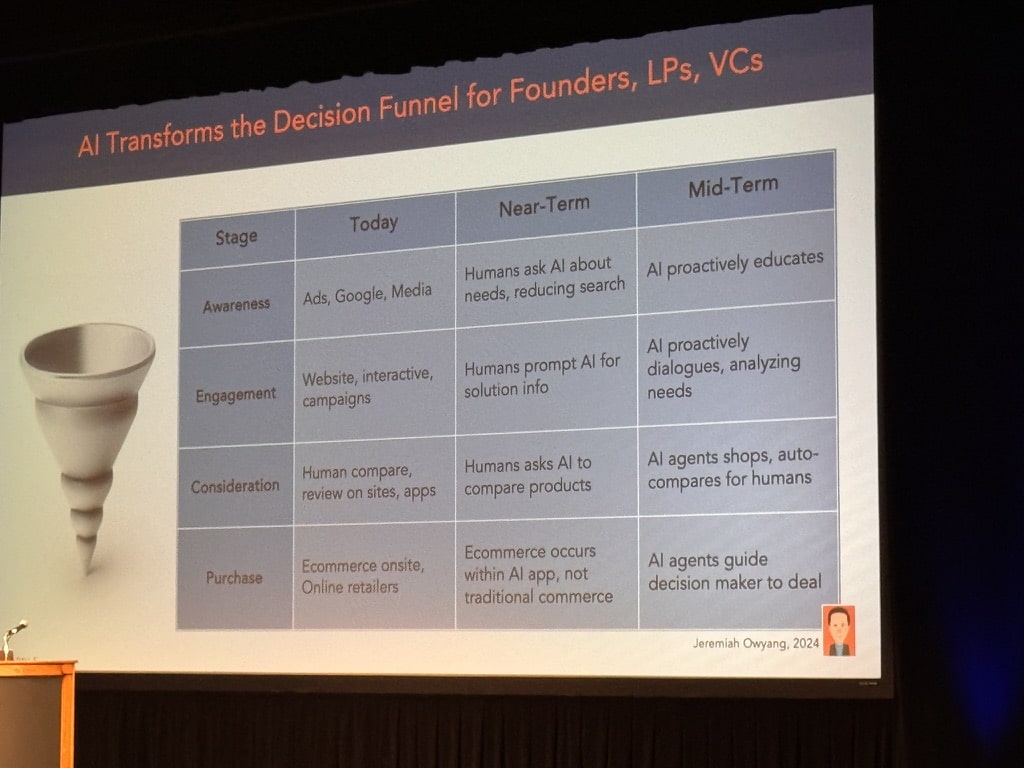
“Land grab exclusive data. Monetize synthetic data.” – Jeremiah Owyang, Blitzscaling Ventures General Partner.
Dr. Muddu Sudhakar, Co-Founder & CEO, Aisera advised to bring AI to data, leave data where it is. Your data is incredibly valuable, that should be encrypted with your keys.
First, build a data set. Second, build an LLM. Third, build applications. (I think he is referring to enterprise vertical use of bespoke GenAI.)
Data should be always in these “traps”:
My question to Jeremiah Owyang, Blitzscaling Ventures General Partner: “I want to know what AI can NOT do: like reading between the lines, implied intent, body language, the combination of emotional, mental, psychological, and other disciplines, and EQ…”
His answer: “AI can do ALL OF THESE!”
I asked him immediately: “Then what does it mean to be human? What is left for humans to enjoy?”
His answer: “I don’t know. That’s the question I ask myself, when I am with my daughter. You asked the BEST question. I don’t have the answer. ” “AI does not have empathy. AI cannot teach or mentor, human to human. In the future, people don’t need to work to make a living. AI will do the work. People will enjoy working as a hobby.”
I’d add that interacting with a machine, no matter how wonderful it is, is never the same as interacting with a human.
The human-to-human relationship is always the most challenging and the most fulfilling to me. Let me quote what Steve Jobs said: “You’ve got to find what you love. And that is as true for your work as it is for your lovers. Your work is going to fill a large part of your life, and the only way to be truly satisfied is to do what you believe is great work. And the only way to do great work is to love what you do.”
This, I can attest: I love technology. It increases productivity, transforms experiences, and grows revenue. But what I love more is the human-to-human mentoring, coaching, consulting; to find the gems, sometimes hidden, in each company, in each person, and empower them to shine their best, as their own brands. I’m passionate about helping AI companies focus on their end-users’ needs and wants (instead of letting engineers decide what the customer journey is), with AI experience design consulting.
As a tech lover, I am wasting no time to adopt and train my AI tools.
But am I going to relinquish to AI my passion, joy, and love for my human-to-human coaching and mentoring? – Heck, NO!
I will never let AI take over the unique, unpredictable, and sometimes magical encounters I have had and will continue to have with my clients. I choose so.
– Will AI bring the end to capitalism, since AI will be working for us, and we get paid for…?
– Will there be only one version of “truth”: AI generated “truth”?
– Will LLM lead to autocracy? Or authoritarianism?
– Will AI make our world a better or worse place for human happiness?
RAG: Retrieval-augmented generation:
https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/what-is-retrieval-augmented-generation/
cRAG: Causal grounding in Causal AI.
LAMs: Large Action Models: hot topic and development in the realm artificial intelligence (AI) is Large Action Models, also referred as Large Agentic Models or LAMs https://medium.com/version-1/the-rise-of-large-action-models-lams-how-ai-can-understand-and-execute-human-intentions-f59c8e78bc09
API: “Application Programming Interface”. In the context of APIs, the word Application refers to any software with a distinct function. Interface can be thought of as a contract of service between two applications. This contract defines how the two communicate with each other using requests and responses.
SLM: SLM stands for Small Language Model, which is a machine learning model in artificial intelligence (AI) that is typically based on a large language model (LLM) but is much smaller in size. SLMs are often trained with domain-specific data and can be used for a variety of tasks, including:
Data engineering: SLMs can help with complex data engineering tasks and specialized problems.
User prompts: SLMs can enrich user prompts and make responses more accurate.
Conversational AI: SLMs can provide quick and relevant responses in real-time, even when operating within the resource constraints of mobile devices or embedded systems.
Small Language Models (SLMs) are compact versions of language models that offer a more efficient and versatile approach to natural language processing. These nimble models play a crucial role in handling data processing efficiently, especially in scenarios where large language models (LLMs) may be overkill.
Grounding: Grounding in AI is the process of connecting abstract knowledge in AI systems to real-world examples, such as by providing models with access to specific data sources. This process can help AI systems produce more accurate, relevant, and contextually appropriate outputs.
RDF: The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) standard originally designed as a data model for metadata. It has come to be used as a general method for description and exchange of graph data. RDF is a standard model for data interchange on the Web. RDF has features that facilitate data merging even if the underlying schemas differ, and it specifically supports the evolution of schemas over time without requiring all the data consumers to be changed.
(Wikipedia:) The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) standard originally designed as a data model for metadata. It has come to be used as a general method for description and exchange of graph data. RDF provides a variety of syntax notations and data serialization formats, with Turtle (Terse RDF Triple Language) currently being the most widely used notation.
RDF is a directed graph composed of triple statements. An RDF graph statement is represented by: 1) a node for the subject, 2) an arc that goes from a subject to an object for the predicate, and 3) a node for the object. Each of the three parts of the statement can be identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI). An object can also be a literal value. This simple, flexible data model has a lot of expressive power to represent complex situations, relationships, and other things of interest, while also being appropriately abstract.
SRAM: Static Random-Access Memory (SRAM) is a popular choice for Artificial Intelligence (AI) chips because it’s fast, reliable, and locally available within the chip, providing instant access to data. SRAM is also compatible with CMOS logic processes, which allows it to track improvements in logic performance as technology advances. However, SRAM can be expensive and consume a lot of energy and space.
SRAM is recommended for small memory blocks and high-speed requirements but comes associated with drawbacks such as its substantial area and increased power consumption. For projects with significant memory requirements, ReRAM offers an advantage owing to its density.
SRAM is made up of flip-flops, which are bistable circuits made up of four to six transistors. Once a flip-flop stores a bit, it keeps that value until it’s overwritten with the opposite value. SRAM comes in two varieties: synchronous and asynchronous. Synchronous SRAMs are synchronized with an external clock signal, and they only read and write information to memory at certain clock states.
SRAM is a locally available memory within a chip. Therefore, it offers instantly accessible data, which is why it is favored in AI applications.
https://semiengineering.com/sram-in-ai-the-future-of-memory/
MLM: Machine Learning Morphism, a building block for designing machine learning workflows. MLM’s have these components: Input space, X , which is modeled as a probability space and has training realizations X . Output space, Y which models the outcome of interest.
Knowledge graph: (Wikipedia:) A knowledge graph formally represents semantics by describing entities and their relationships. Knowledge graphs may make use of ontologies as a schema layer. By doing this, they allow logical inference for retrieving implicit knowledge rather than only allowing queries requesting explicit knowledge.
Wrapper: In the context of AI, a “wrapper” typically refers to a piece of software or code that encapsulates or wraps around another piece of code or a system, providing a simplified or standardized interface for interacting with it.
For example, in machine learning, a wrapper might be used to encapsulate a complex algorithm or model, allowing it to be easily integrated into a larger software system without the need for the developers to understand all the details of how the algorithm works.
In other contexts, a wrapper might be used to provide additional functionality or features around an existing system, such as logging, error handling, or security.
Overall, wrappers are often used to simplify the process of integrating different components or systems within a larger software application or framework.
MOAT: In the context of AI, “MOAT” typically stands for “Model of Adversarial Training.” Adversarial training is a technique used in machine learning to improve the robustness and resilience of models against adversarial attacks.
In this context, a “moat” refers metaphorically to a protective barrier surrounding a castle or fortress. Just as a physical moat defends a castle from attackers, a “Model of Adversarial Training” helps defend machine learning models from adversarial attacks by training them on adversarially perturbed examples.
The goal of adversarial training is to expose the model to small, carefully crafted perturbations to input data during the training process. This helps the model learn to make more robust predictions, even when faced with adversarial examples designed to fool it.
Data base vector: A vector database stores pieces of information as vectors. Vector databases cluster related items together, enabling similarity searches and the construction of powerful AI models. https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/ai/what-is-vector-database/
RPA: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a software technology designed to simplify the creation, deployment, and management of software bots that mimic human actions and interactions with digital systems and software.
OCR: “Optical Character Recognition.” It is a technology that recognizes text within a digital image. It is commonly used to recognize text in scanned documents and images. OCR software can be used to convert a physical paper document, or an image into an accessible electronic version with text.
(Feel free to add more.)
© Joanne Z. Tan All rights reserved.
====================================================================================
– To stay in the loop, subscribe to our Newsletter
– Download free Ebook
Please don’t forget to like it, comment, or better, SHARE IT WITH OTHERS, – they will be grateful!
(About 10 Plus Brand: In addition to the “whole 10 yards” of brand building, digital marketing, and content creation for business and personal brands. To contact us: 1-888-288-4533.)
– Visit our Websites:
Phone: 888-288-4533
– Find us online by clicking or follow these hashtags:
